SDK vs API: Understanding the Difference in Software Development
In software development, SDKs (Software Development Kits) and APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are fundamental tools that simplify and enhance the development process. While both are essential, they serve distinct purposes and are used in different scenarios. Let’s dive into the definitions, types, and differences between SDKs and APIs.
What is an SDK?
An SDK, or Software Development Kit, is a comprehensive collection of tools, libraries, documentation, and sample code that helps developers create applications from scratch. It provides everything needed to streamline the development process. With an SDK, developers can avoid starting from zero and focus on integrating features efficiently.
Key Features of SDKs:
- Includes tools like compilers, debuggers, and emulators.
- Often comes with an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) for seamless integration.
- Provides pre-built components to accelerate development.
Types of SDKs:
SDKs are categorized based on their platform or purpose:
- Mobile SDKs: Designed for mobile app development (e.g., iOS SDK, Android SDK).
- Web SDKs: For integrating web applications with third-party services (e.g., Google Maps SDK).
- Game SDKs: Used for developing games with specific engines (e.g., Unity SDK).
- Cloud SDKs: For interacting with cloud services (e.g., AWS SDK, Google Cloud SDK).
Examples of Popular SDKs:
- Facebook SDK : Enables integration of Facebook features into apps.
- Stripe SDK: Provides tools for payment processing.
- TensorFlow SDK: Aids in machine learning and neural network projects.
- Google Analytics SDK: Tracks user behavior in applications.
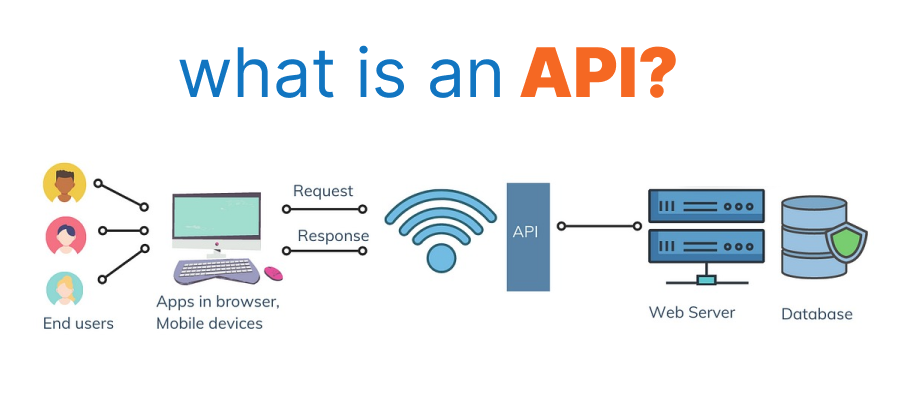
What is an API?
An API, or Application Programming Interface, is a set of protocols and rules that enable communication between software components. APIs define how applications interact with each other, specifying the methods and data formats for exchanging information.
Key Features of APIs:
- Facilitates integration with external services.
- Simplifies the implementation of complex functionalities through API calls.
- Promotes modular and scalable application design
Types of APIs:
APIs can be classified into various categories based on their architecture and purpose:
- REST APIs: Use HTTP requests for CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete).
- SOAP APIs: Employ XML-based messaging for communication.
- GraphQL APIs: Allow clients to request specific data through queries.
- WebSocket APIs: Enable real-time communication between clients and servers.
Examples of Popular APIs:
- Twitter API: Provides access to Twitter data and functionalities.
- Google Maps APIEmbeds interactive maps into applications.
- OpenWeatherMap API: Supplies weather data for app integration.
- Spotify API: Grants access to Spotify’s music catalog and user data.
SDK vs API: Key Differences
| Aspect | SDK | API |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A toolkit with tools, libraries, and documentation for app development. | A set of protocols enabling communication between software. |
| Purpose | Helps in building applications from scratch. | Facilitates interaction with external services or functionalities. |
| Components | Includes compilers, debuggers, and sample code. | Includes endpoints and data formats for communication. |
| Use Case | Ideal for comprehensive app development. | Best for integrating specific features or accessing data. |
| Examples | Android SDK, AWS SDK, Unity SDK | Twitter API, Google Maps API, Spotify API. |
When to Use an SDK vs API
- API: Use an API when you need to access specific functionalities or data from another service. For example, integrating a payment gateway or fetching weather data
- SDK: Opt for an SDK when you require a complete toolkit to build an application or integrate deeply with a platform. For instance, developing a mobile app using the Android SDK.
Conclusion
SDKs and APIs play complementary roles in modern software development. While APIs focus on enabling connectivity and communication, SDKs provide the tools and resources to build applications efficiently. Understanding their differences and use cases ensures you choose the right solution for your development needs, fostering productivity and seamless integration.